| [1] 赵瑞梅,孙永平.强直性脊柱炎患者外周血TNF-α、IL-17、IL-23的表达及相关性分析[J].实用临床医药杂志,2015,19(9):38-40.
[2] 叶文芳,刘健,汪四海.强直性脊柱炎患者血清免疫球蛋白亚型、细胞因子的变化及相关性分析[J].免疫学杂志,2015,31(4): 362-365.
[3] 王作龙,钟乃风,马莉.检测不同活动期强直性脊柱炎患者外周血Th1、Th2和Treg细胞的意义[J].贵阳医学院学报,2015,40(4): 363-367
[4] 林洁华,黄闰月,江泽波,等.补肾强督治偻方对脂多糖刺激的小鼠RAW264.7细胞炎性细胞因子表达的影响[J].广州中医药大学学报,2015,32(2):285-289.
[5] Frauendorf E, von Goessel H, May E, et al. HLA-B27-restricted T cells from patients with ankylosing spondylitis recognize peptides from B*2705 that are similar to bacteria-derived peptides. Clin Exp Immunol. 2003;134(2): 351-359.
[6] 姜洋子.软骨干/祖细胞的特性及其促进关节软骨修复再生的研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2012.
[7] 魏璐婉.hBMP-6基因修饰的骨髓间充质干细胞治疗类风湿性关节炎的实验研究[D].济南:山东大学,2012.
[8] 李治,毕平,刘伟,等.关于干细胞关节腔内注射修复软骨损伤的研究与进展[J].中外健康文摘,2014,11(6):276-277.
[9] 谭学新.强直性脊柱炎患者血免疫球蛋白、炎症指标及血液流变学指标的检测及临床意义[J].医学理论与实践,2015,28(11): 1426-1428.
[10] 岳枫,胡波.人类白细胞抗原、信号转导和转录激活因子、整合素与自身免疫病的相关性研究进展[J].中国医药导报,2015,12(14): 31-35.
[11] Neidhart M, Baraliakos X, Seemayer C, et al. Expression of cathepsin K and matrix metalloproteinase 1 indicate persistent osteodestructive activity in long-standing ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68(8): 1334-1339.
[12] Xueyi L, Lina C, Zhenbiao W, et al. Levels of circulating Th17 cells and regulatory T cells in ankylosing spondylitis patients with an inadequate response to anti-TNF-α therapy. J Clin Immunol. 2013;33(1):151-161.
[13] Chen MH, Chen WS, Lee HT, et al. Inverse correlation of programmed death 1 (PD-1) expression in T cells to the spinal radiologic changes in Taiwanese patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Rheumatol. 2011;30(9):1181-1187.
[14] 李萍,王庆文.白细胞介素-23受体基因多态性与强直性脊柱炎遗传易感性关系的荟萃分析[J].中国药物与临床,2015,15(6): 756-761.
[15] Ciccia F, Accardo-Palumbo A, Alessandro R, et al. Interleukin-22 and interleukin-22-producing NKp44+ natural killer cells in subclinical gut inflammation in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(6):1869-1878.
[16] Wong-Baeza I, Ridley A, Shaw J, et al. KIR3DL2 binds to HLA-B27 dimers and free H chains more strongly than other HLA class I and promotes the expansion of T cells in ankylosing spondylitis. J Immunol. 2013;190(7):3216-3224.
[17] 崔保刚.比较与分析不同影像学检测方法用于诊断强直性脊柱炎骶髂关节病变效果[J].中国CT和MRI杂志,2015,13(5):25-28.
[18] Slobodin G, Kessel A, Kofman N, et al. Phenotype of resting and activated monocyte-derived dendritic cells grown from peripheral blood of patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Inflammation. 2012;35(2):772-775.
[19] Zhao SS, Hu JW, Wang J, et al. Inverse correlation between CD4+ CD25high CD127low/- regulatory T-cells and serum immunoglobulin A in patients with new-onset ankylosing spondylitis. J Int Med Res. 2011;39(5):1968-1974.
[20] Ciccia F, Accardo-Palumbo A, Giardina A, et al. Expansion of intestinal CD4+CD25(high) Treg cells in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a putative role for interleukin-10 in preventing intestinal Th17 response.Arthritis Rheum. 2010; 62(12):3625-3634.
[21] Prevosto C, Goodall JC, Hill Gaston JS. Cytokine secretion by pathogen recognition receptor-stimulated dendritic cells in rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol. 2012;39(10):1918-1928.
[22] 程艳伟,李清山,杨坤,等.诱导性多潜能干细胞治疗骨关节炎的研究进展[J].中华医学杂志,2015,95(17):1354-1357.
[23] 崔云鹏,曹永平,刘恒.骨髓间充质干细胞治疗大鼠骨关节炎的实验研究[J].北京大学学报:医学版,2015,47(2):211-218.
[24] 王黎明,周建军,白雯,等.脐带间充质干细胞治疗17 例类风湿性关节炎患者的临床疗效观察[J].中国免疫学杂志,2010,26(7): 659-662.
[25] 刘鹄,任明亮,王潇娉,等.强直性脊柱炎患者骨髓间充质干细胞的生物学及免疫学特性[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2012,22(6): 559-565.
[26] 舒强.类风湿关节炎,强直性脊柱炎和骨关节炎滑膜成纤维样细胞增殖与分化的体外研究[D].济南:山东大学,2006.
[27] 张荣华,欧阳菁.肾主骨生髓理论与骨髓间充质干细胞骨向分化[C].2007年全国中西医结合强直性脊柱炎专题研讨会论文集, 2007:83-87.
[28] 张华勇,冯学兵,王丹丹,等.异基因骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗克罗恩病一例[J].中华医学杂志,2009,89(36):2590.
[29] 袁恒锋.Notch1-Hes信号通路在强直性脊柱炎髋关节韧带中的关联研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2013.
[30] 徐薇,欧阳桂芳,冯鸣.自体外周血干细胞移植治疗急性髓细胞白血病合并强直性脊柱炎一例[J].中华内科杂志,2000,39(5):327.
[31] Glintborg B, Østergaard M, Krogh NS, et al. Clinical response, drug survival and predictors thereof in 432 ankylosing spondylitis patients after switching tumour necrosis factor α inhibitor therapy: results from the Danish nationwide DANBIO registry. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72(7):1149-1155.
[32] Wu Y, Ren M, Yang R, et al. Reduced immunomodulation potential of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells induced CCR4+CCR6+ Th/Treg cell subset imbalance in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(1):R29.
[33] Lai NS, Yu HC, Chen HC, et al. Aberrant expression of microRNAs in T cells from patients with ankylosing spondylitis contributes to the immunopathogenesis Clin Exp Immunol. 2013;173(1):47-57.
[34] Bidad K, Salehi E, Jamshidi A, et al. Effect of all-transretinoic acid on Th17 and T regulatory cell subsets in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol. 2013;40(4):476-483.
[35] 宋庆林.间充质干细胞治疗强直性脊柱炎36例临床分析[J].中国医学装备,2014,11(8):183-184.
[36] 刘鹄,任明亮,王潇娉,等.强直性脊柱炎患者骨髓间充质干细胞的生物学及免疫学特性[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2012,22(6): 559-565.
|
.jpg)

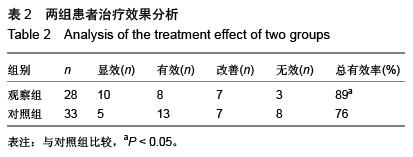
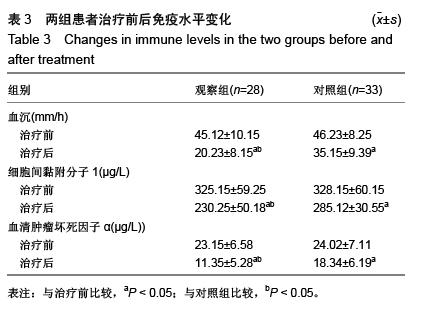
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
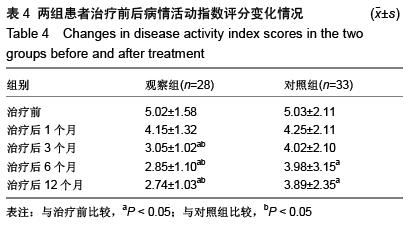
.jpg) 2.6 不良事件 观察组患者有1例在治疗过程中出现注射外渗现象,经重新选择血管后顺利完成注射。2例患者出现轻微发热现象,经积极物理降温之后体温恢复至正常水平。术后患者均未出现呕吐、肝肾功能异常等情况。对照组有5例患者在治疗过程中出现轻微恶心现象,未予以特殊处理,均随时间推移自行消失。其余患者均未出现任何不良反应。
2.6 不良事件 观察组患者有1例在治疗过程中出现注射外渗现象,经重新选择血管后顺利完成注射。2例患者出现轻微发热现象,经积极物理降温之后体温恢复至正常水平。术后患者均未出现呕吐、肝肾功能异常等情况。对照组有5例患者在治疗过程中出现轻微恶心现象,未予以特殊处理,均随时间推移自行消失。其余患者均未出现任何不良反应。